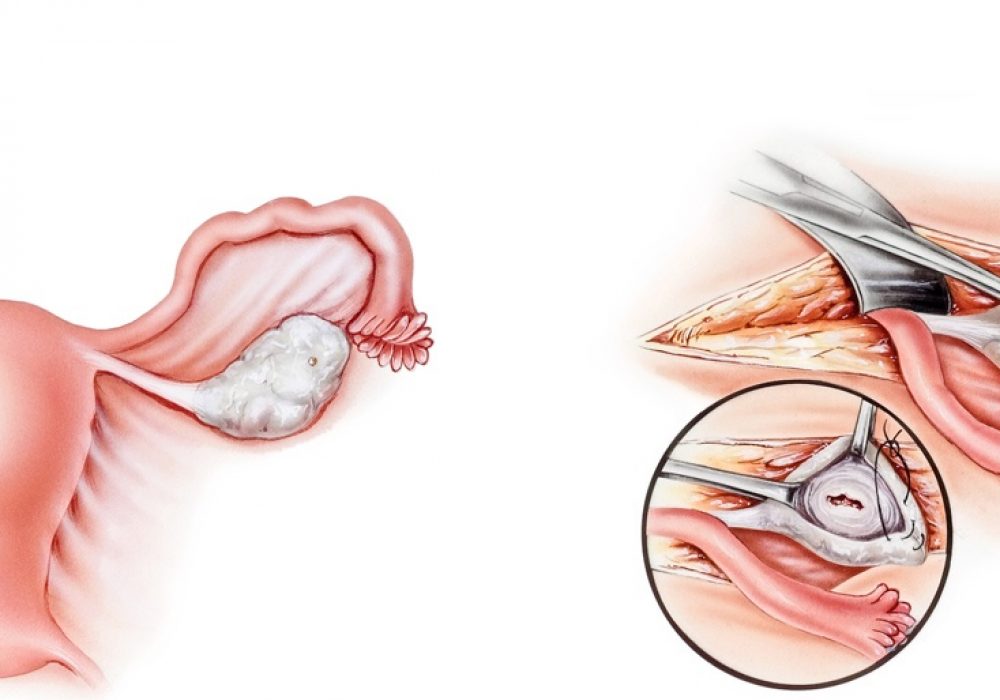
An ovarian cystectomy can be performed in one of two ways.
ABDOMINAL SURGERY
Your doctor will make a large incision in your abdomen and conduct open surgery through the incision. This is often a good choice if there is the possibility of cancer since the large opening gives the doctor a clear view of all the pelvic organs.
LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY
In this procedure, a few small incisions in the abdomen are made and surgical tools are inserted through these holes. One instrument is called a laparoscope. It is a thin, flexible instrument with a lighted camera at the end, which guides the surgeon through the procedure. The tissue is removed through these small incisions. Both procedures are performed under general anaesthesia. Generally, an abdominal surgery carries greater risks for infection or damage to tissue. However, it is a better choice when there is a large amount of tissue to be removed, or if the organs need to be seen clearly. Laparoscopic surgeries usually have quicker healing times and the patient experiences less pain.